For a long time, battery life has been a core performance factor for electronic devices such as smartphones. A major breakthrough in silicon anode battery technology has significantly improved battery energy density—its theoretical specific capacity is approximately 10 times that of traditional graphite anodes. This means that without increasing the battery volume, the device’s battery life can be greatly enhanced. With the widespread application of silicon anode batteries in the market, the maximum battery capacity of mainstream smartphones has increased directly from 5000mAh to over 7500mAh, boosting battery life by 1.5 times. However, due to the low shutdown voltage characteristic of silicon anode batteries, the battery’s operating voltage has dropped from a minimum of 3V to 2.5V or even lower. This imposes higher requirements on driver ICs, which now need to operate within a wider power supply range while ensuring consistent performance.
Awinic has launched the 6th-generation high-voltage linear motor driver IC AW86938SCSR, featuring an ultra-low UVLO (Under-Voltage Lockout) of 2V and hardware-level battery protection technology. This product perfectly adapts to silicon anode batteries: even as the device’s shutdown voltage continues to decrease, it prevents system failures caused by high-current draw at low battery levels and ensures stable motor operation. Additionally, it integrates AAE 2.0 and LCC 3.0 technologies to deliver precise haptic feedback, enabling smooth vibration responses for incoming calls, gaming, and music playback.
Product Features
-
Wide voltage input: 2.3~5.5V
-
Ultra-low UVLO: 2.0V
-
Multi-level battery protection support
-
LCC 3.0 function support
-
AAE 2.0 support
-
Low power mode
-
I2S/TDM interface support
-
ACH & AGH support
-
Motor fast start-stop algorithm support
-
Motor internal resistance detection
-
Smart Loop function (for small-size motor applications)
-
Ultra-fast response time: 1ms
-
LCC accuracy: ±1Hz
-
8.8Vout @ VBAT=4.2V, 8Ω Loading
-
Standby current: 4.5μA
-
UVP (Under-Voltage Protection), OCP (Over-Current Protection), OTP (Over-Temperature Protection) functions
Package Information

Table 1: AW86938SCSR Package Information Table
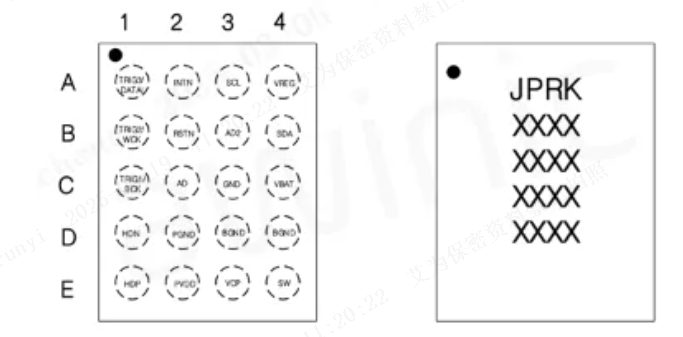
Figure 1: AW86938S Pin Map & Top Mark Diagram
Typical Application Diagram
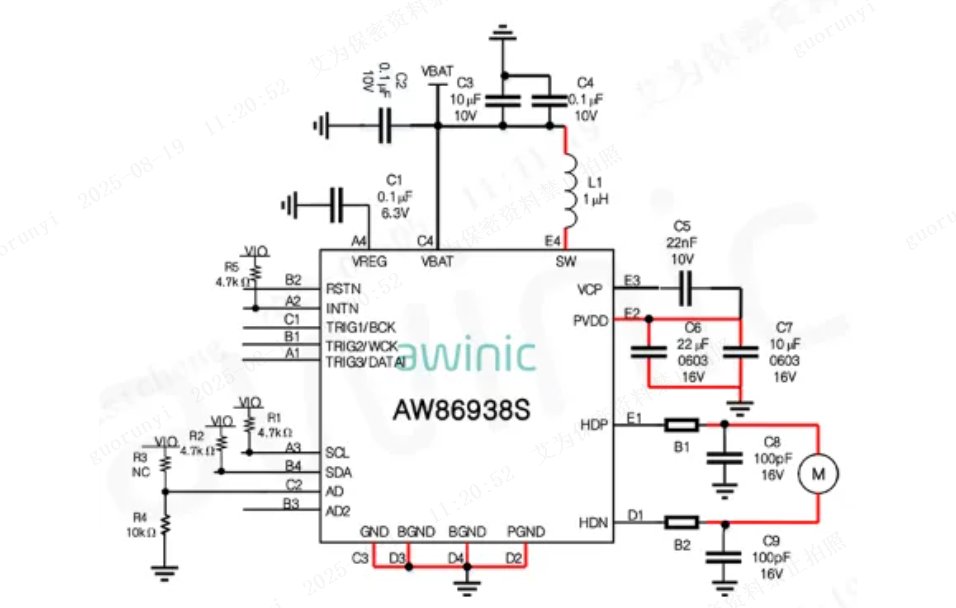
Figure 2: AW86938S Typical Application Diagram
Application Scenarios

Figure 3: Simulated Application Scenario Diagrams
Key Features
1. Multi-Level Battery Protection
With the adoption of silicon anode batteries in high-end flagship devices, the battery shutdown voltage of smartphones is decreasing. The battery protection function prevents instantaneous high-current draw at low battery levels (which could cause system crashes) and ensures the IC’s supply voltage never drops below the UV (Under-Voltage) threshold—guaranteeing normal motor operation even at low battery. The AW86938S’s proprietary hardware-level battery protection function enables smoother motor output, better haptic feedback, and lower noise when the battery is low.
Images
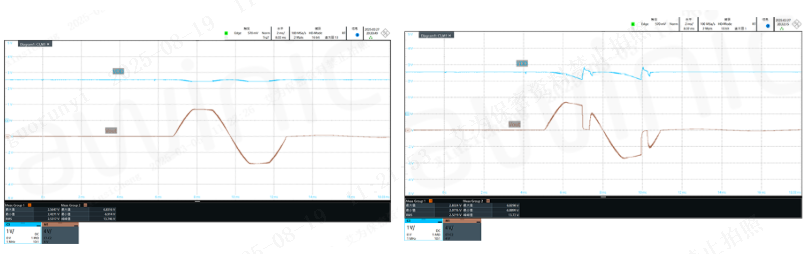
Figure 4: Battery Protection Enabled Diagram Figure 5: Battery Protection Disabled Diagram
2. Fast Start-Stop with No Overshoot at Any Frequency
By leveraging the LRA (Linear Resonant Actuator) model for precise motor parameter detection, the IC uses algorithms to overdrive arbitrary waveforms—effectively avoiding overshoot issues with off-resonance waveforms. Additionally, when combined with AAE technology, it achieves perfect square-wave vibration, further optimizing the haptic effect. The diagrams below show the effect waveforms at 120Hz, 160Hz, and 200Hz: the first half represents the original acceleration waveform, and the second half shows the processed waveform.
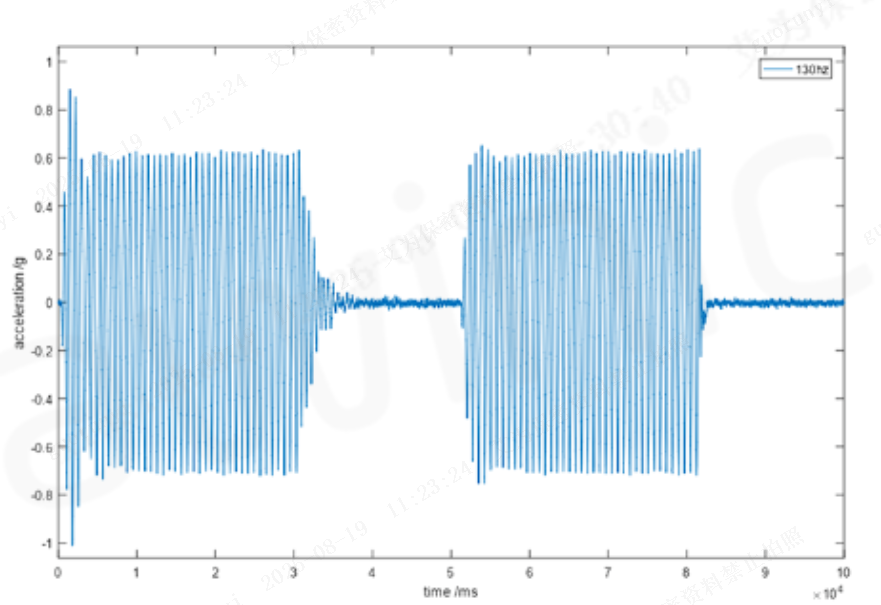
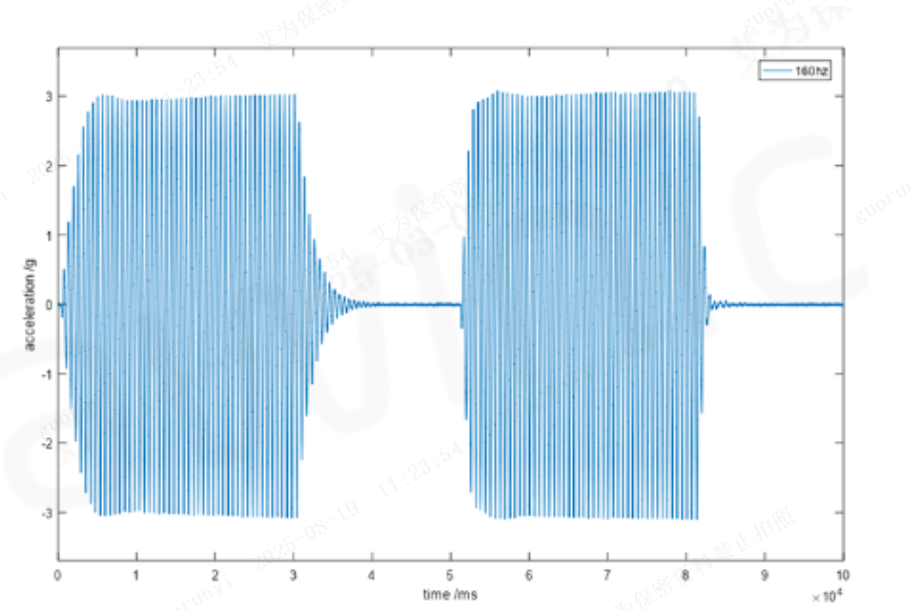
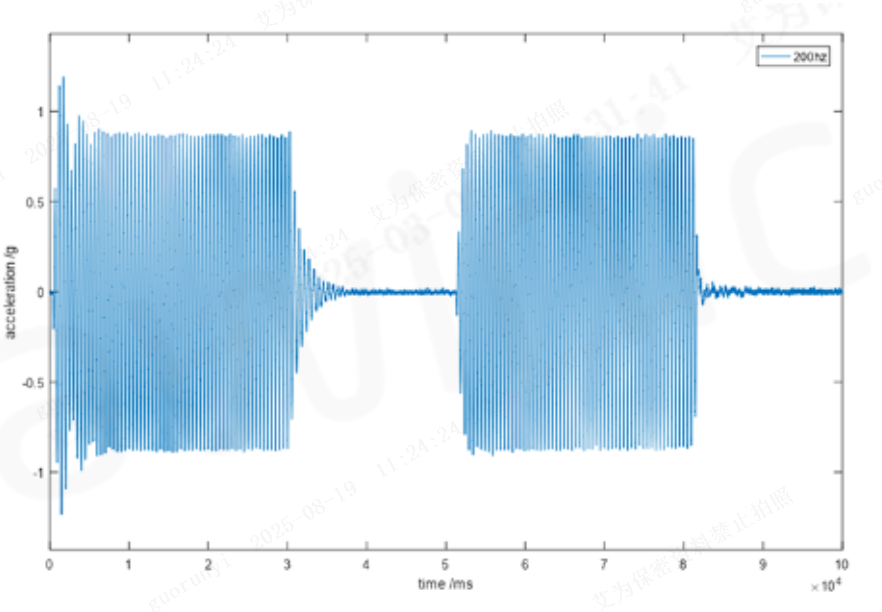
Figure 6: Fast Start-Stop Diagrams at Different Frequencies
3. ACH and AGH
For content-side haptic experiences, Awinic’s ACH (Audio-Controlled Haptics) and AGH (Audio-Generated Haptics) deliver an innovative solution:
-
Haptic ACH revolutionizes incoming call experiences. Instead of uniform ringtones, it matches diverse vibration patterns to different contacts and custom ringtones—gentle vibrations simulate the delicate feel of a friend’s tap, while strong vibrations convey the urgency of important calls. Whether using an I2C or I2S interface, Awinic’s ACH solution ensures strict synchronization between sound and vibration.
-
AGH uses algorithms to automatically and accurately convert music into delicate vibrations, turning every music listening session into a unique sensory experience.
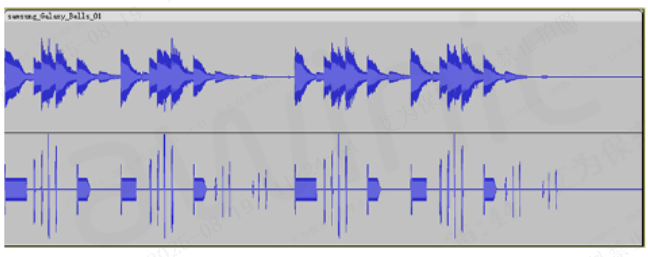
Figure 7: ACH Audio-Vibration Synchronization
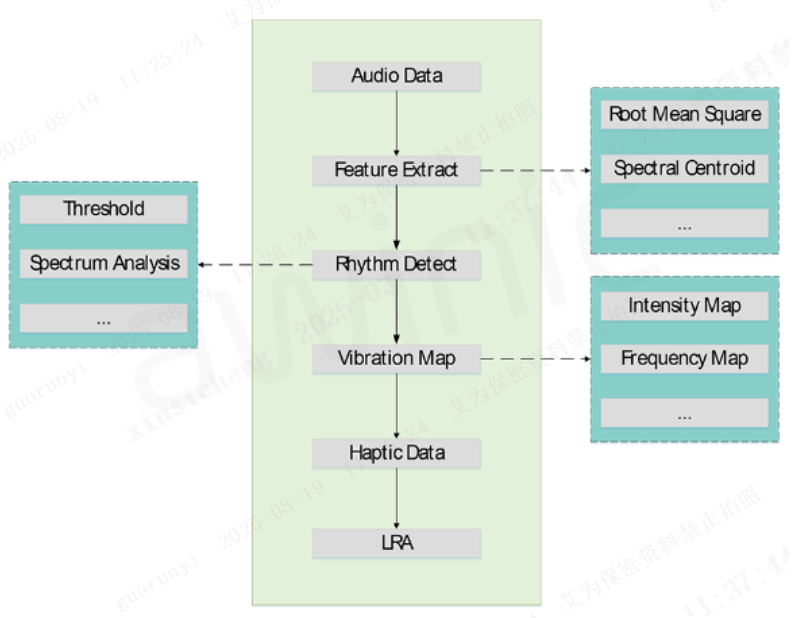
Figure 8: AGH Basic Framework Diagram
Conclusion
As a pioneer in the haptics industry, Awinic leverages its profound technical accumulation to continuously innovate in core technologies such as piezoelectric driving and vibration simulation algorithms. The company is fully exploring the boundaries of haptic perception, refining every haptic feedback solution to create high-quality haptic experiences. Whether it’s the delicate vibration alert for incoming calls or the precise force feedback during gaming, users can truly feel the unique technological charm brought by advanced technology at every moment of device operation—driving the industry’s haptic experiences to new heights.
Key Terminology Glossary
-
Silicon Anode Battery: A type of lithium-ion battery that uses silicon-based materials for the anode (instead of traditional graphite), offering significantly higher energy density but lower shutdown voltage.
-
UVLO (Under-Voltage Lockout): A protection function in ICs that shuts down the device when the supply voltage drops below a preset threshold, preventing damage from under-voltage operation.
-
LCC (LRA Closed-Loop Control): A technology that monitors and adjusts the motor’s resonant frequency in real time to maintain optimal vibration performance (LCC 3.0 represents an upgraded version with enhanced precision).
-
AAE (Advanced Amplitude Enhancement): An algorithm that optimizes vibration amplitude and waveform to improve haptic feedback quality (AAE 2.0 is an updated iteration with better performance).
-
LRA (Linear Resonant Actuator): A type of linear motor commonly used in smartphones for haptic feedback, operating at a specific resonant frequency for efficient vibration.
-
ACH (Audio-Controlled Haptics): A technology that synchronizes vibration patterns with audio signals (e.g., ringtones) to create context-aware haptic feedback.
-
AGH (Audio-Generated Haptics): A technology that converts audio data (e.g., music) into corresponding vibration signals in real time for immersive sensory experiences.









